Exploring the Importance of Different Distance Metrics in Machine Learning
Today I learned 😂😂 I found this post on LinkedIn and I think this is helpful. In numerous real-world scenarios, ML algorithms are utilized for tasks like image classification, image recognition, and information retrieval based on image content. Selecting an appropriate distance metric plays a crucial role in these applications as it enables algorithms to identify similarities between different image contents. So, I believe that the better you understand the foundation of the ML models you use, the better you use them.
What? According to a basic mathematical definition (source: Wikipedia), a distance metric utilizes a distance function to establish a measurement of the relationship between individual elements within a dataset.
For me, during my classes, I notice that professors frequently mentioned distance metrics, but I often overlooked their significance as I didn’t consider them particularly helpful.
Why important?
- Several supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms rely on distances, including k-means clustering and k-nearest neighbors.
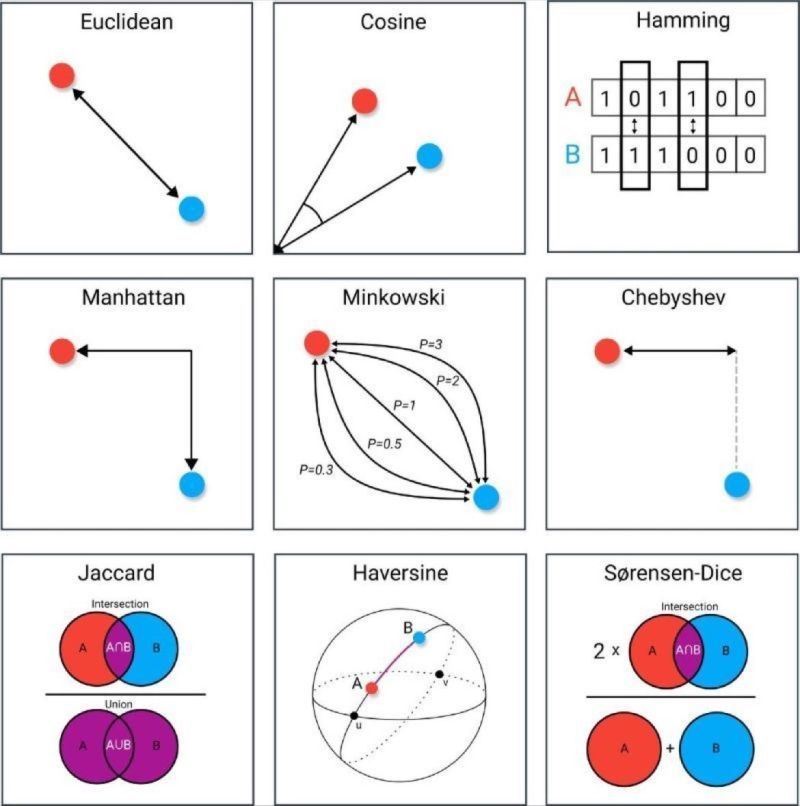
- Among the commonly used distance metrics, Euclidean distance is the most popular. However, there are other distance metrics like Manhattan distance, Chebyshev distance, and Minkowski distance, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
- For instance, the Manhattan distance is useful when the dimensions in the data have different units of measurement, while the Chebyshev distance is suitable for applications where the maximum difference between two dimensions is more important. Please read the post for more details on other examples.
- Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each distance metric is crucial in selecting the appropriate one for a specific problem. By choosing the right distance metric, we can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of our ML models.
I think an example will make this easier to understand, because I need an example to understand this.
Again, distance metrics’ primary purpose is to measure the similarity between data points, which significantly impacts the performance of machine learning models, be it for classification tasks or clustering.
Imagine you are working on creating clusters using algorithms like K-Means Clustering or the k-nearest neighbor algorithm (cliche 🤭), which leverages nearest neighbors for solving classification or regression problems. How would you determine the similarity between different observations? How can we establish that the two points are similar? The answer lies in assessing the similarity of their features. When these points are plotted, their closeness or distance from each other becomes apparent.
Therefore, we calculate the distance between data points and utilize it to define their similarity. Now, the question arises: How do we compute this distance, and what are the various distance metrics employed in machine learning? Do these metrics differ based on the type of learning problem? Do we apply any specific theorems for this purpose? These are all important queries that highlight the significance of understanding the distance metrics used in machine learning.
Some popular distances you may have heard of before are: Euclidean, Manhattan, Minkowski, or Hamming distances. You can start looking at these distances first.
Copied from DataR Labs
Types of commonly used distance metrics There are many types of distance metrics used in data science, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most commonly used distance metrics include:
- Euclidean distance: This is the straight-line distance between two points in a multi-dimensional space. It is the most commonly used distance metric and is suitable for continuous variables.
- Manhattan distance: Also known as taxicab distance, it measures the distance between two points by adding the absolute differences of their coordinates. It is useful for discrete variables.
- Minkowski distance: This is a generalized distance metric that includes Euclidean and Manhattan distance as special cases. It is defined as the pth root of the sum of the pth power of the absolute differences between coordinates.
- Cosine similarity: This metric measures the cosine of the angle between two vectors. It is used for text data and other sparse data where the magnitude of the vector is less important than the direction.
- Chebyshev distance: Chebyshev distance, also known as chessboard distance or L∞ distance, is a metric used to measure the distance between two points in a grid system where movement is restricted to horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions.
- Hamming distance: This is a metric used for comparing two strings of equal length. It measures the number of positions at which the corresponding symbols are different.